A new era of synthetic
affinity reagents
Smart polymers go beyond the limitations of biologics to offer new possibilities in CGT analytics and downstream processing
Smart polymers are non-biological synthetic affinity reagents that are rationally designed and chemically produced to go beyond the limits of their biological counterparts. By utilising a combination of advanced in silico and in vitro epitope discovery, smart polymers are strategically designed to target a specific region of a virus or cell to best suit the end application. This can range from high affinity binding for analytics, to lower affinity binding for affinity chromatography. Read on to learn how these novel affinity reagents are designed and manufactured and how they deliver innovative solutions to advanced therapy manufacture.
How are smart polymers designed and why is it so important?
Developing biological affinity reagents such as antibodies has a major flaw – its random. Development depends on an immune response, and elements such as the binding region or the binding affinity cannot be predicted or controlled. The term ‘antibody lottery’ is a good fit! Smart polymers on the other hand are rationally designed to meet the specific needs of the end application. This process starts with in silico and/or in vitro molecular modelling
This process starts with in silico and/or in vitro molecular modelling…
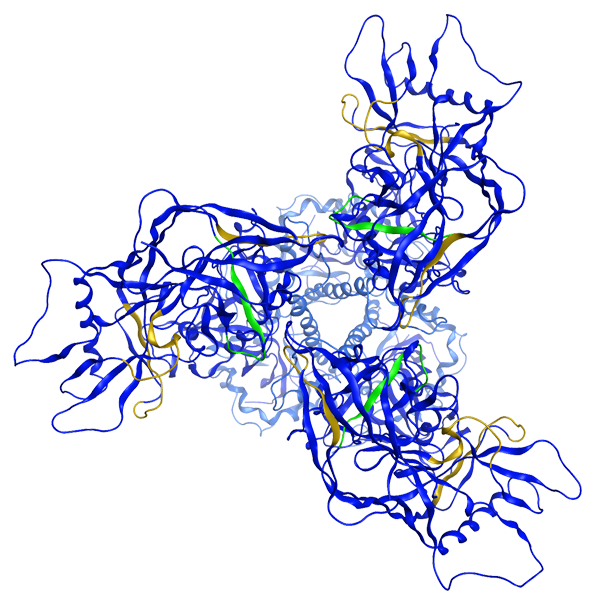
In silico modelling
Pioneering computational chemistry tools are used to model the 3D target structure. Loops, beta sheets and alpha-helix structures are assessed alongside solvent accessibility. This process identifies the best epitopes for reagent development.
In vitro epitope discovery
A unique approach to in vitro epitope discovery can also be used alongside this to identify and confirm the best epitopes. During this process, the entire target molecule is exposed to monomers which only bind to accessible surface epitopes. The target molecule is then digested and washed away to leave the monomer complexes (polymers) bound with the accessible epitope peptide sequence. This is then released and sequenced using mass spectrometry.
Monomer screening
The next step is to identify the most appropriate building blocks; monomers. A library of over 600 monomers is screened against the identified epitope(s). During this stage, features such as binding positions, binding strength, and monomer properties are assessed to choose the most suitable monomers to take through to production.
What are the benefits of smart polymers?
Smart polymers are truly novel synthetic affinity solutions that push the boundaries of what’s currently possible.
Designed in silico.
- Our pioneering computational chemistry means we can screen the full surface of any viral particle, engineered or not, to identify optimally exposed epitopes and produce synthetic affinity reagents that are truly novel.
- We have access to over 600 monomer building blocks (versus the traditional 20 amino acids) allowing us to build-in the exact functionality needed for the application.
Synthesized chemically.
- The chemical manufacturing process of smart polymers means we can deliver a new wave of synthetic affinity reagents that go beyond the capabilities of biologics, providing safe, reproducible and scalable affinity solutions to our clients.
- Smart polymers are free of Animal Derived Components (ADCs), reducing the risk of leached ligands on product quality and safety.
- Robust purification formats allow for sterilization, increased cleanability and re-use potential.
Deployed with confidence.
- Smart polymers offer new solutions to solving high value bioprocessing challenges for our clients. We are using our technology to go beyond what is currently possible.
- Large batch sizes, rapid scale up and manufacturing consistency means clients can depend on the smart polymer supply chain.